Define Sea Floor Spreading And Its Significance For Oceanic Crust
Seafloor spreading theory that oceanic crust forms along submarine mountain zones known collectively as the mid ocean ridge system and spreads out laterally away from them.
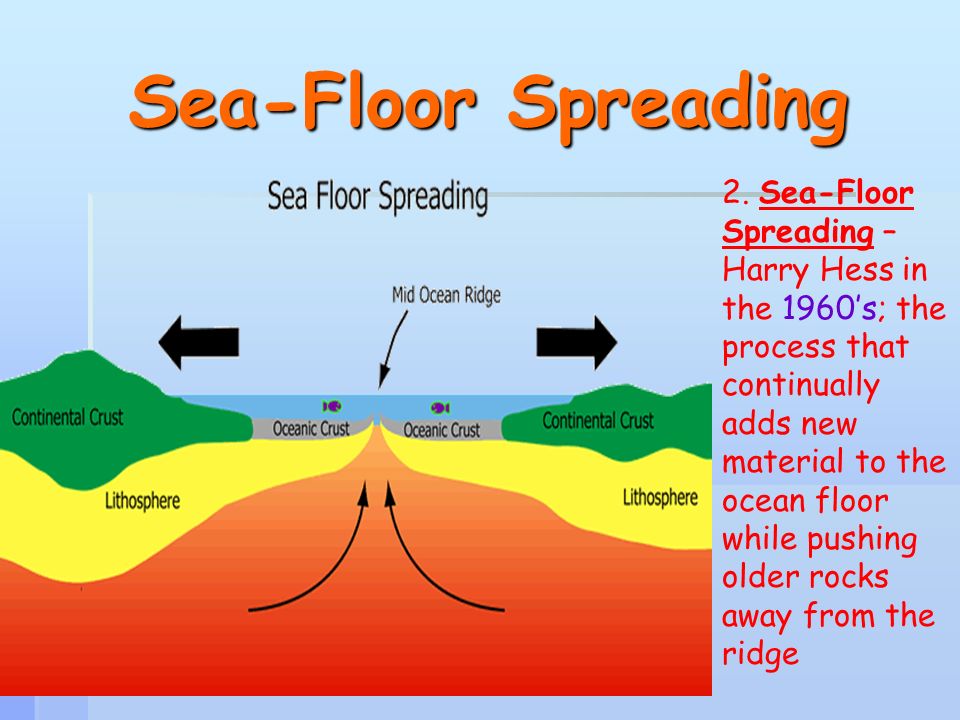
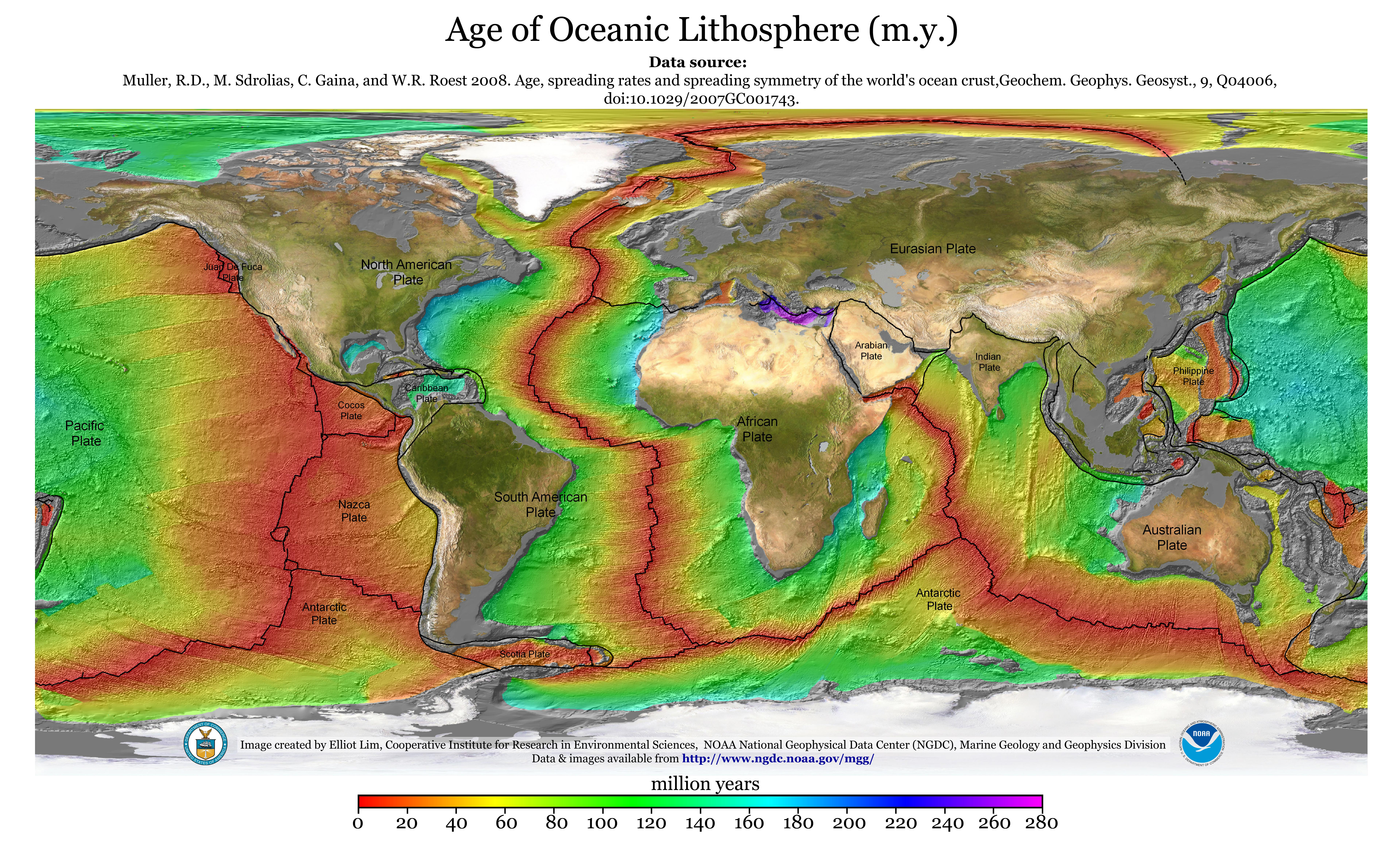
Define sea floor spreading and its significance for oceanic crust. Seafloor spreading is a geologic process where there is a gradual addition o. The magnetism of mid ocean ridges helped scientists first identify the process of seafloor spreading in the early 20th century. The mid ocean ridge is the region where new oceanic crust is created. Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of a tectonic plate it is composed of the upper oceanic crust with pillow lavas and a dike complex and the lower oceanic crust composed of troctolite gabbro and ultramafic cumulates.
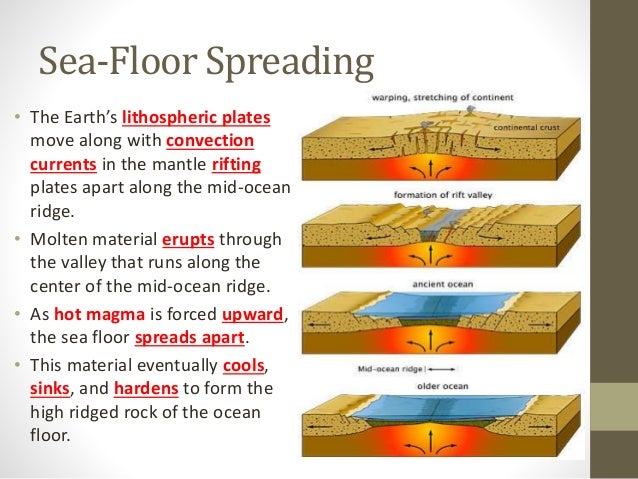
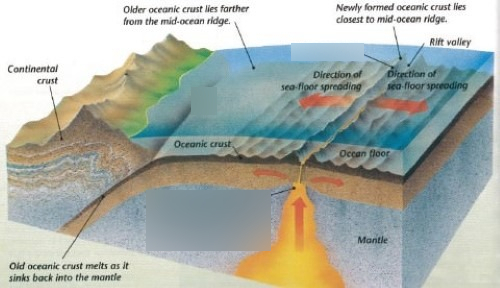
These age data also allow the rate of seafloor spreading to be determined and they show that rates. This idea played a pivotal role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics which revolutionized geologic thought during the last quarter of the 20th century. The oceanic crust is composed of rocks that move away from the ridge as new crust is being formed. New oceanic crust forms from cooling and crystallization of lava that flows out of this divergent plate boundary from earth s interior.
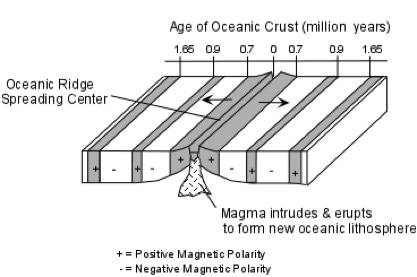
The rate at which new oceanic lithosphere is added to each tectonic plate on either side of a mid ocean ridge is the spreading half rate and is equal to half of the spreading rate. Spreading rate is the rate at which an ocean basin widens due to seafloor spreading. N a series of processes in which new oceanic lithosphere is created at oceanic ridges spreads away from the ridges and returns to the earth s interior. As upwelling of magma continues the plates continue to diverge a process known as seafloor spreading samples collected from the ocean floor show that the age of oceanic crust increases with distance from the spreading centre important evidence in favour of this process.
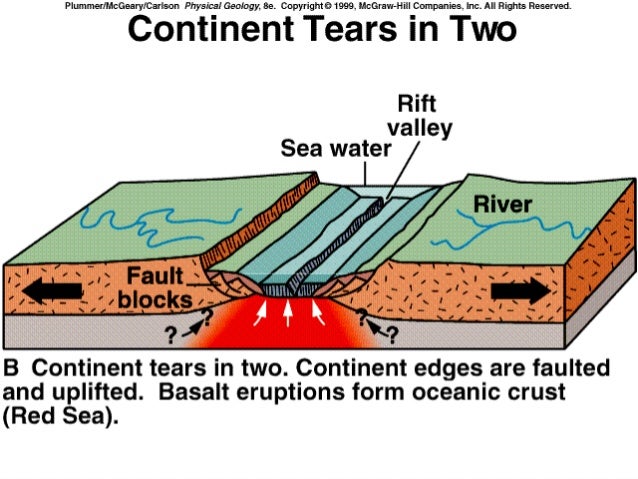
The process of sea floor spreading. Seafloor spreading is a process that occurs at mid ocean ridges where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge. Sea floor spreading involves divergence of adjacent tectonic plates on the ocean bottom caused by convection currents in the mantle. Spreading rates determine if the ridge is fast intermediate or slow.
Define sea floor spreading and its significance for oceanic crust. Basalt the once molten rock that makes up most new oceanic crust is a fairly magnetic substance and scientists began using magnetometers to measure the magnetism of the ocean floor in the 1950s what they discovered was that the magnetism of the ocean floor around. The crust overlies the solidified and uppermost layer of the mantle the crust and the solid mantle layer together constitute oceanic lithosphere.