Define Seafloor Spreading And Its Significance For Oceanic Crust
Unlike wegener he was able to see his seafloor spreading hypothesis largely accepted and confirmed as knowledge of the ocean floor increased dramatically.
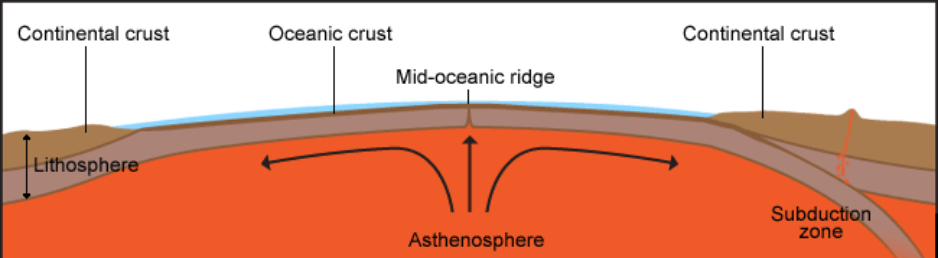
Define seafloor spreading and its significance for oceanic crust. The formation of the new crust is due to the rising of the molten material magma from the mantle by convection current. Sea sea floor spreading see flr flohr the process by which the sea floor is being continuously. Seafloor spreading definition a process in which new ocean floor is created as molten material from the earth s mantle rises in margins between plates or ridges and spreads out. Seafloor spreading is a geologic process where there is a gradual addition o.
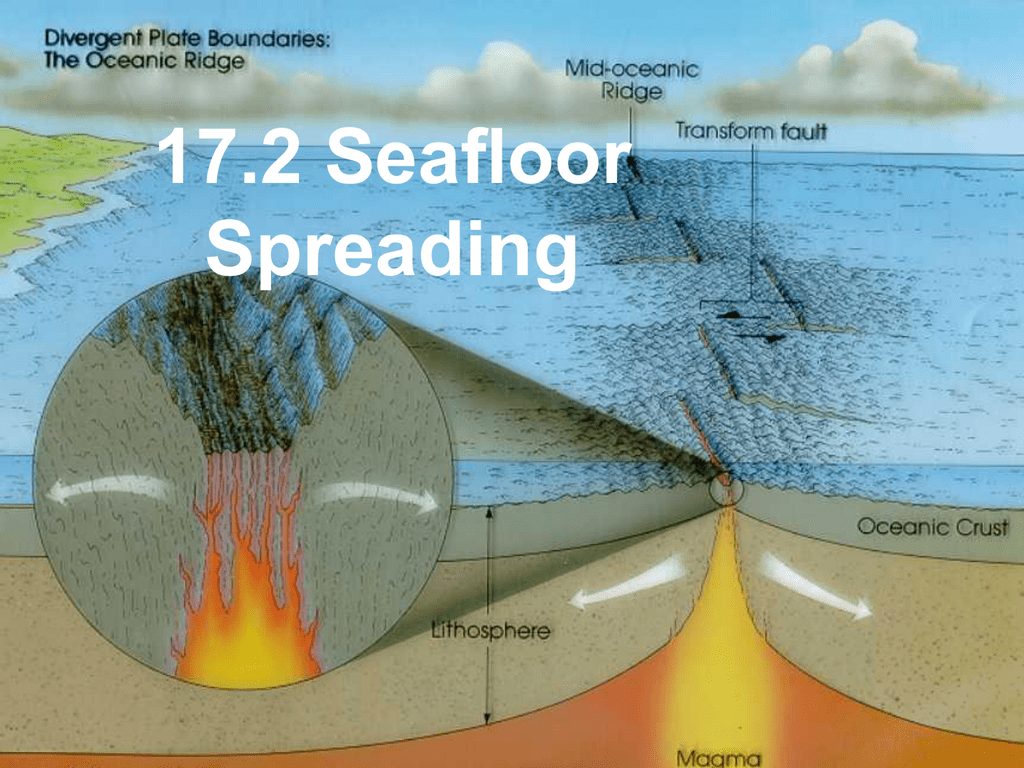
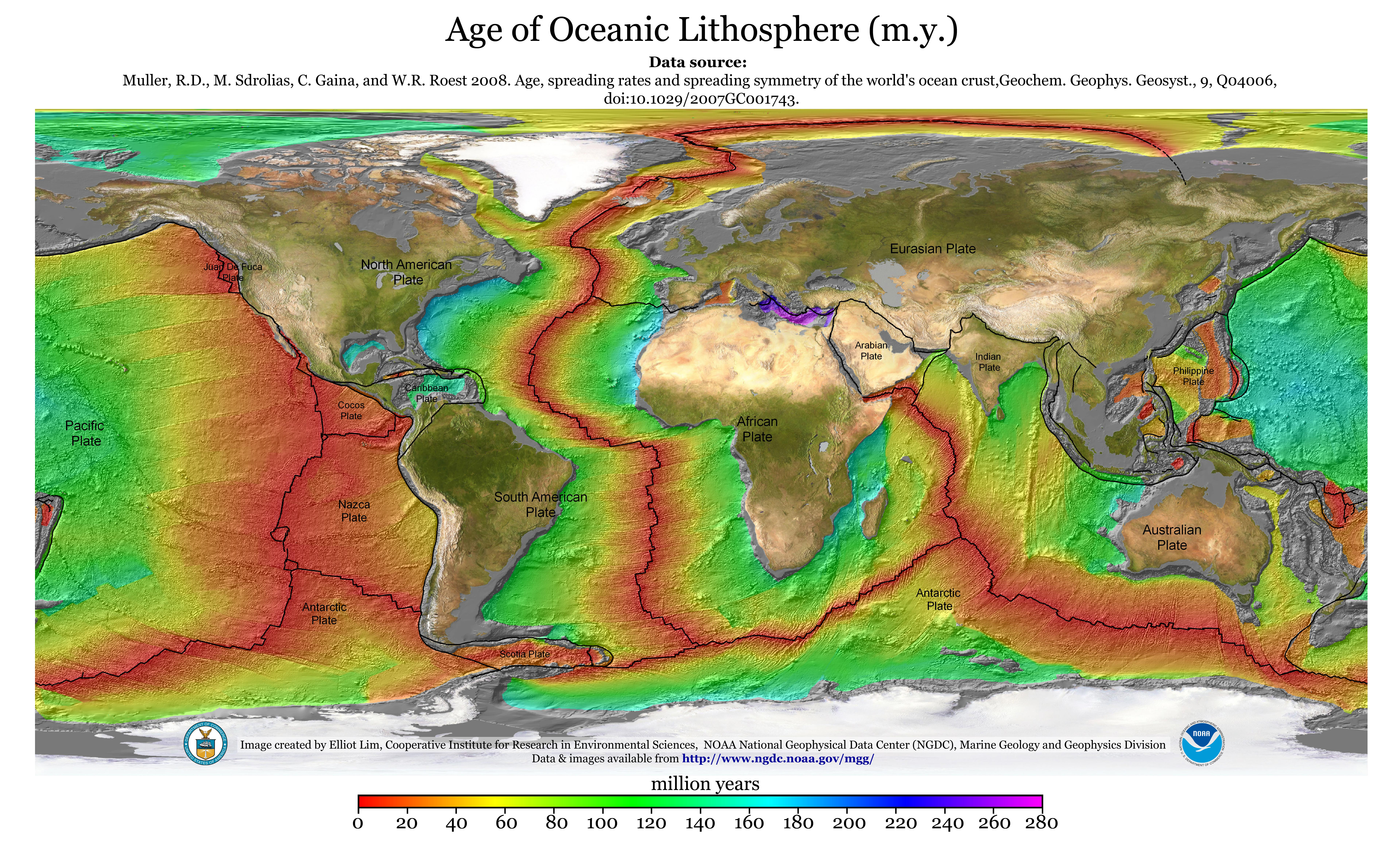
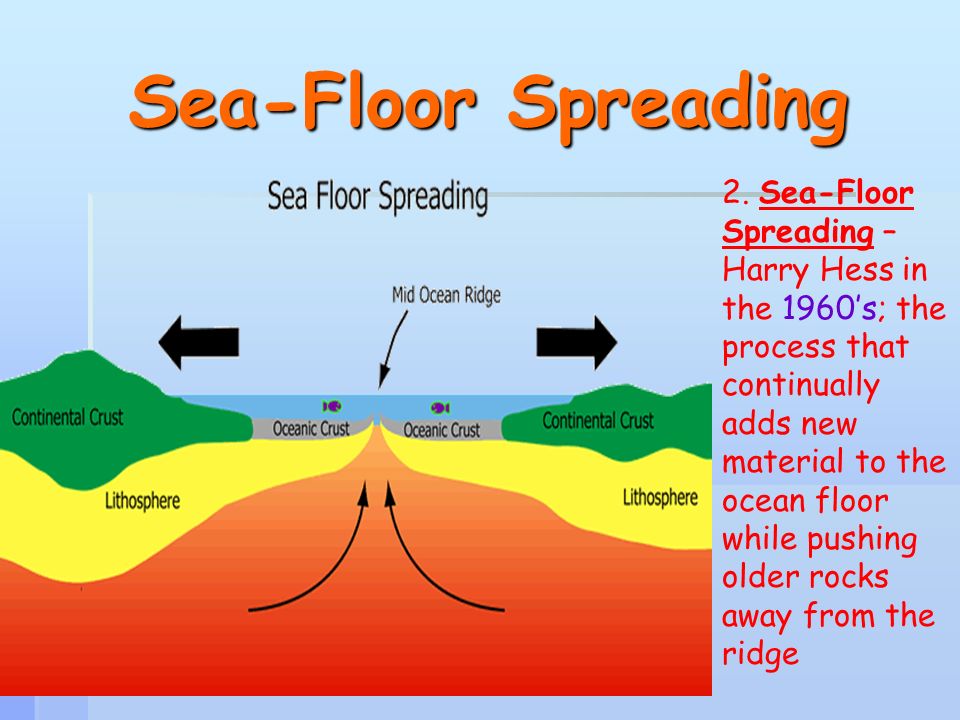
World war ii gave scientists the tools to find the mechanism for continental drift that had eluded wegener. Seafloor spreading is a process that occurs at mid ocean ridges where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge. When oceanic plates diverge tensional stress causes fractures to occur in the lithosphere. The motivating force for seafloor spreading ridges is tectonic plate slab pull at subduction zones rather than magma pressure although there is.
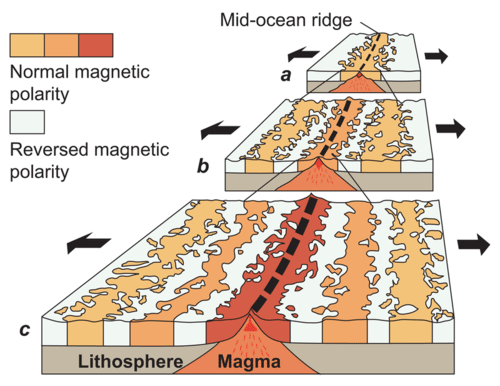
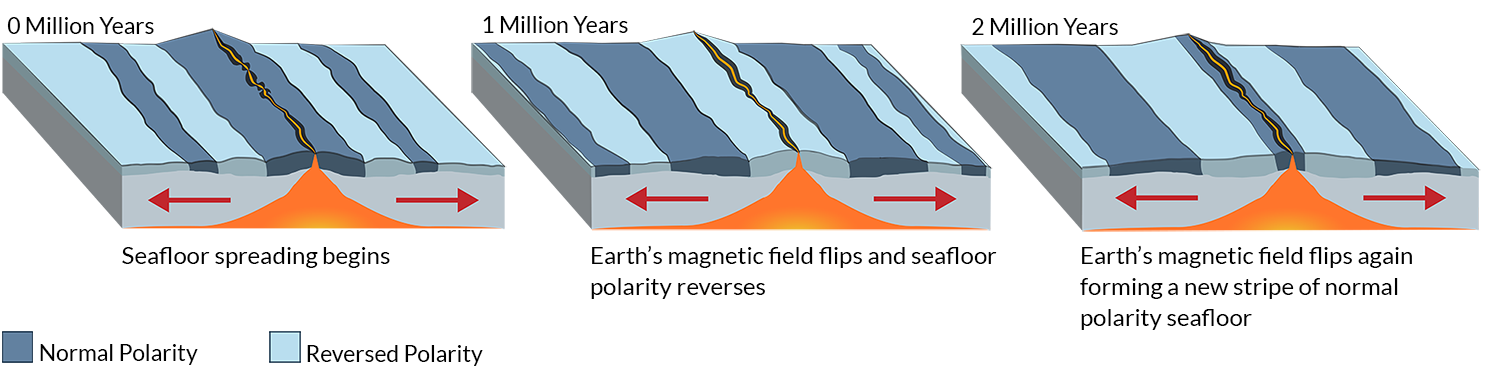
The magnetism of mid ocean ridges helped scientists first identify the process of seafloor spreading in the early 20th century. Seafloor spreading helps to explain continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics. New oceanic crust forms from cooling and crystallization of lava that flows out of this divergent plate boundary from earth s interior. Define sea floor spreading and its significance for oceanic crust.
The process of sea floor spreading. The oceanic crust is composed of rocks that move away from the ridge as new crust is being formed. His basic idea of seafloor spreading along mid oceanic ridges has well withstood the test of time. Basalt the once molten rock that makes up most new oceanic crust is a fairly magnetic substance and scientists began using magnetometers to measure the magnetism of the ocean floor in the 1950s what they discovered was that the magnetism of the ocean floor around.
This idea played a pivotal role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics which revolutionized geologic thought during the last quarter of the 20th century. Maps and other data gathered during the war allowed scientists to develop the seafloor spreading hypothesis this hypothesis traces oceanic crust from its origin at a mid ocean ridge to its destruction at a deep sea trench and is the mechanism for continental drift. Hess who served for years as the head of princeton s geology department died in 1969. Seafloor spreading theory that oceanic crust forms along submarine mountain zones and spreads out laterally away from them.